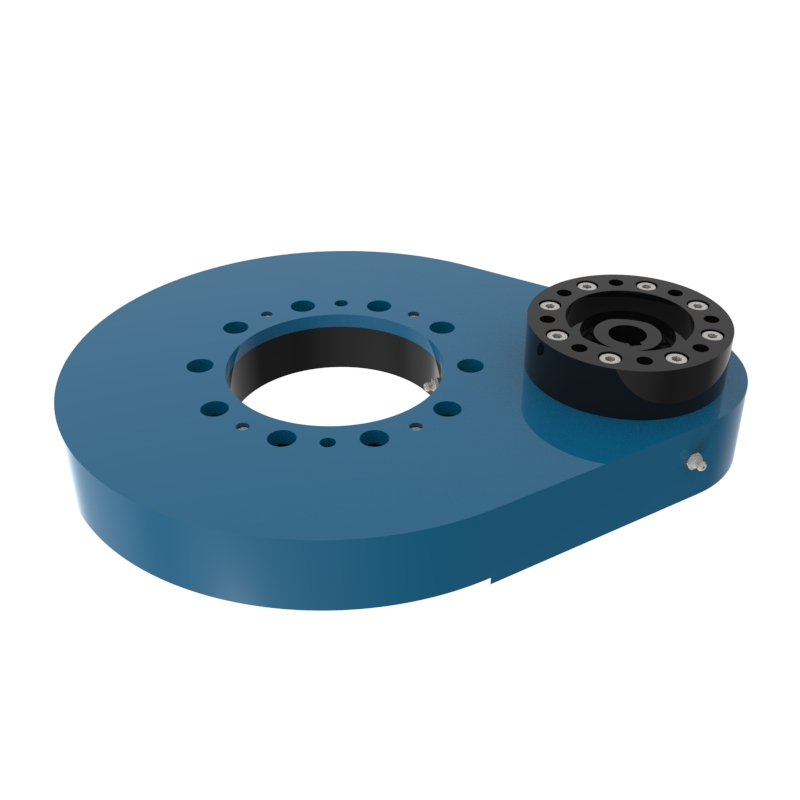
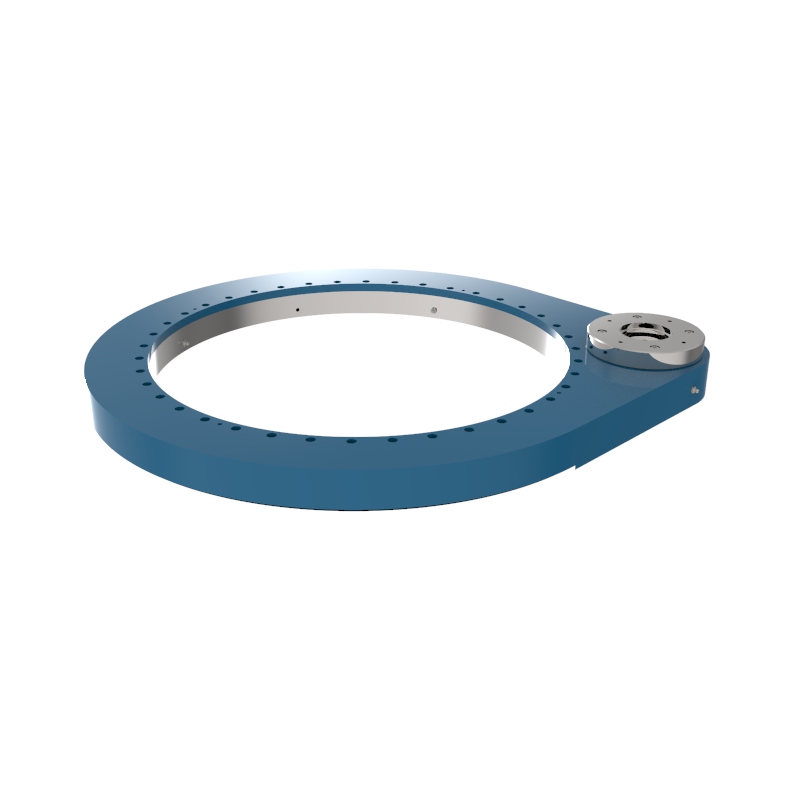
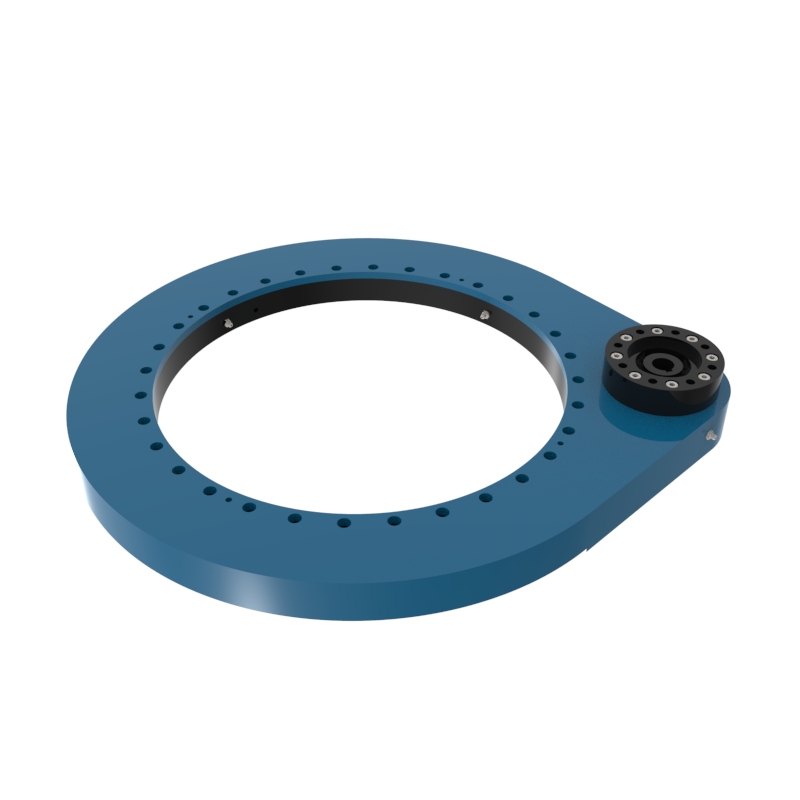
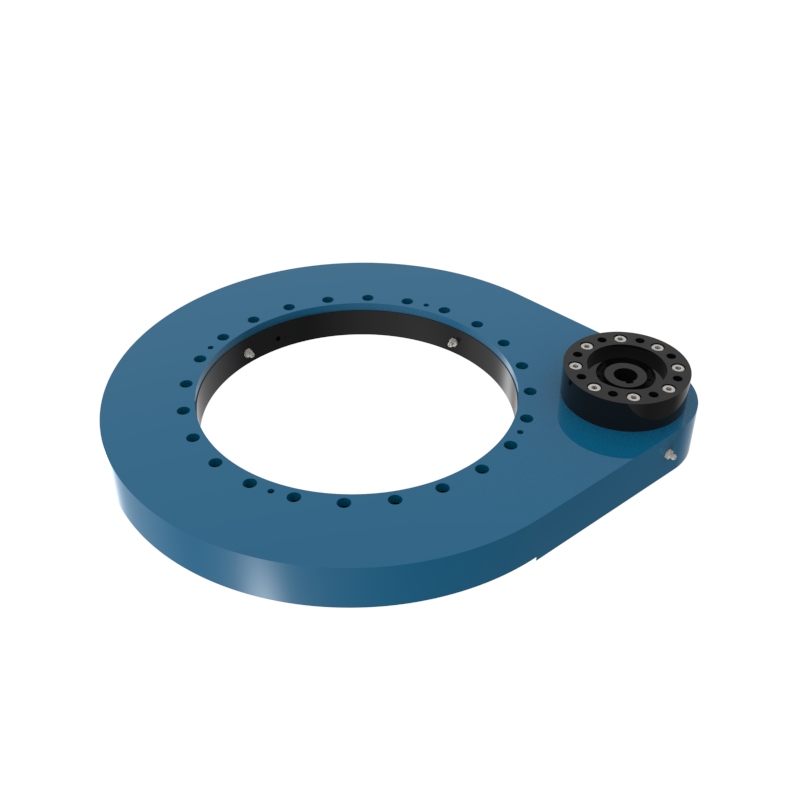
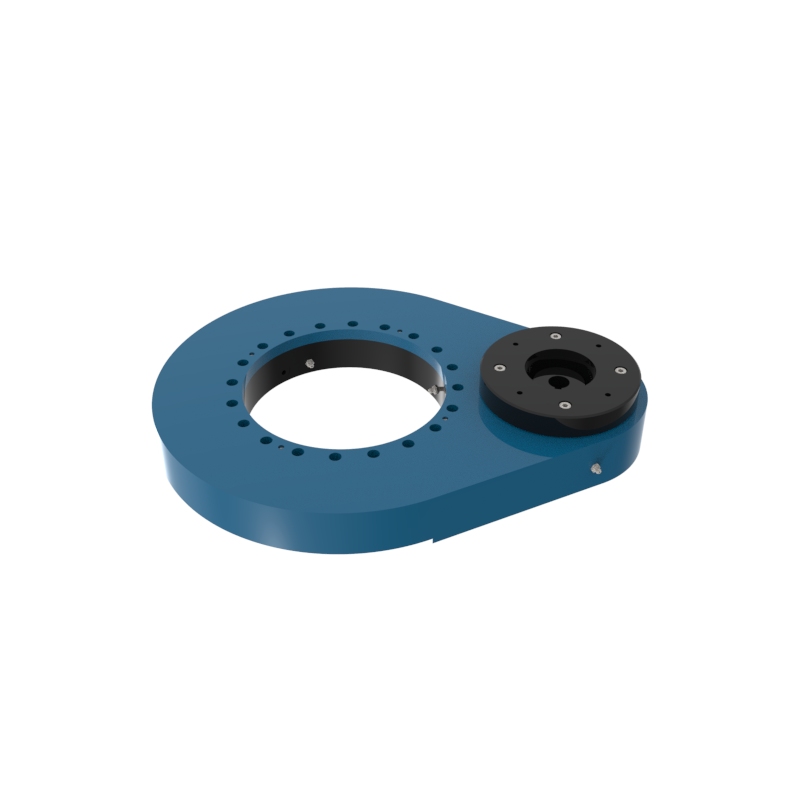
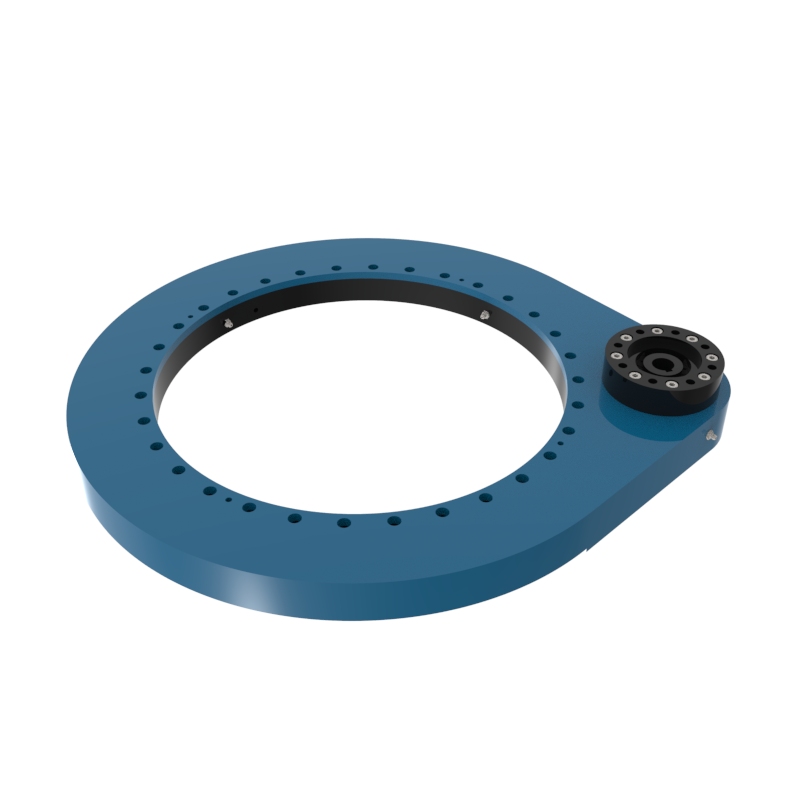
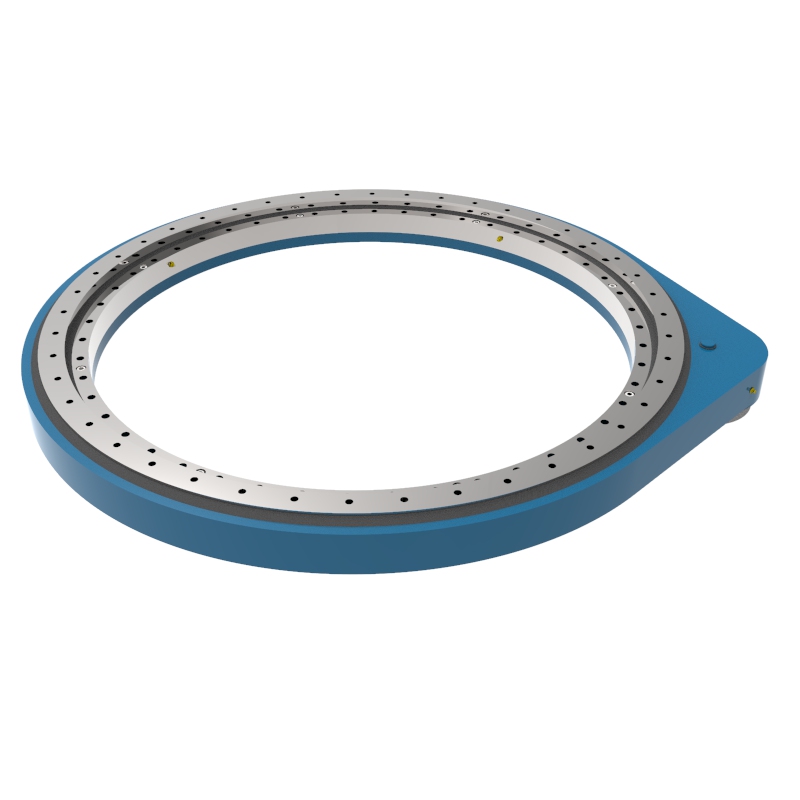
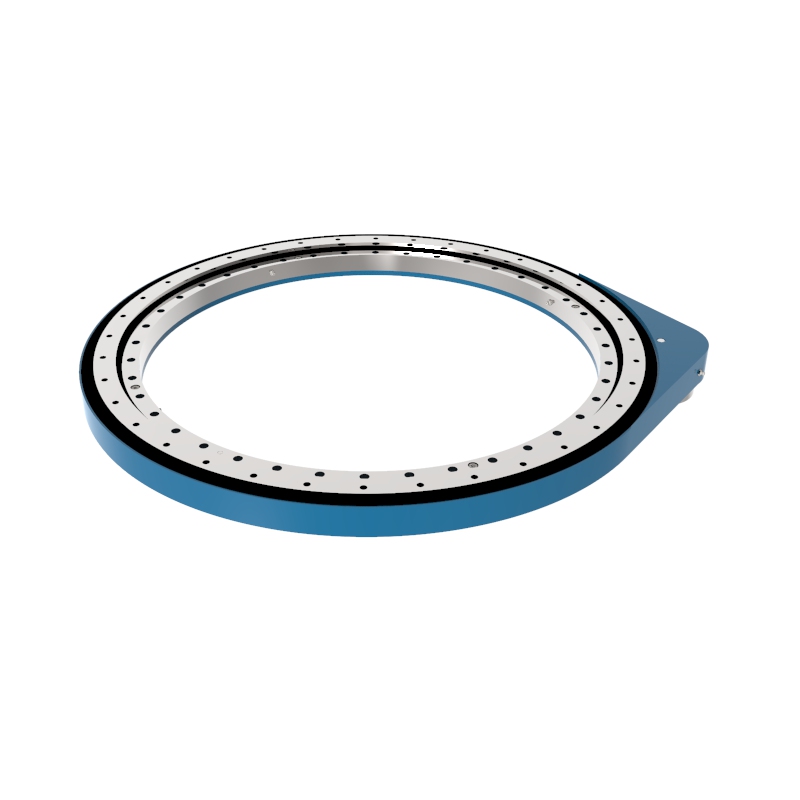
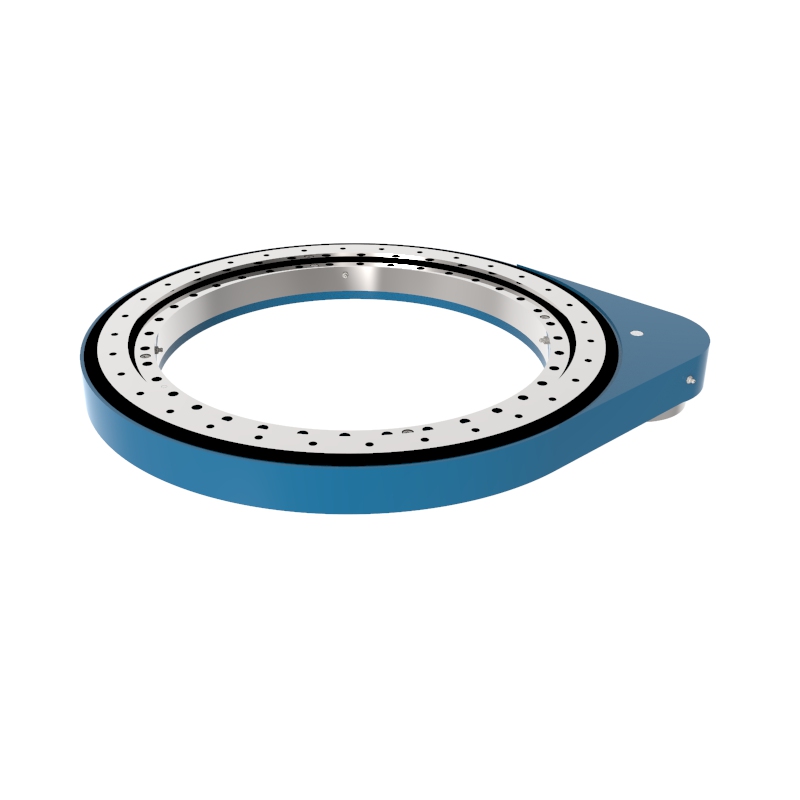
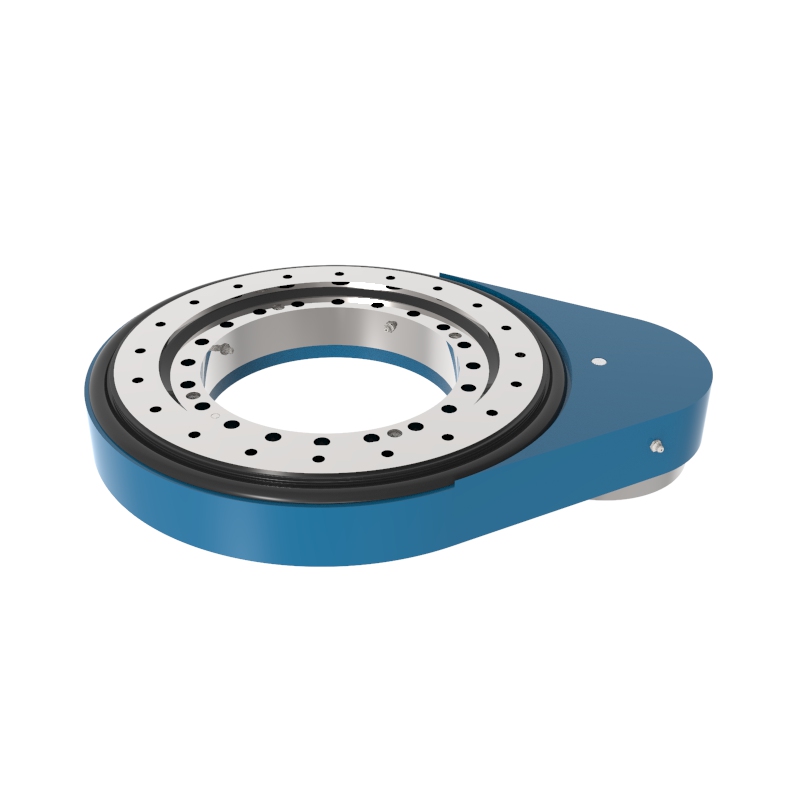
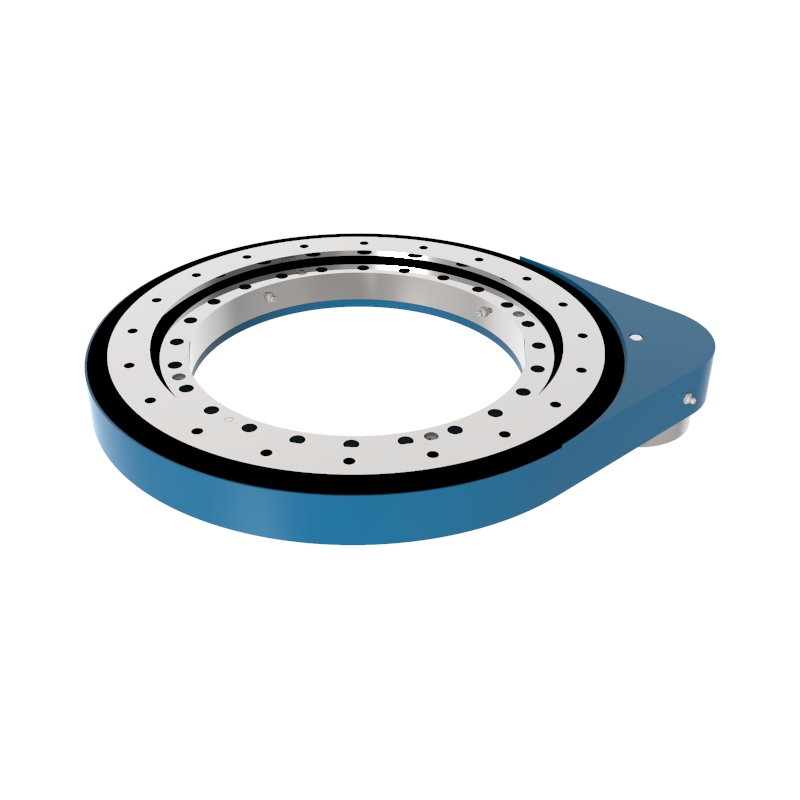
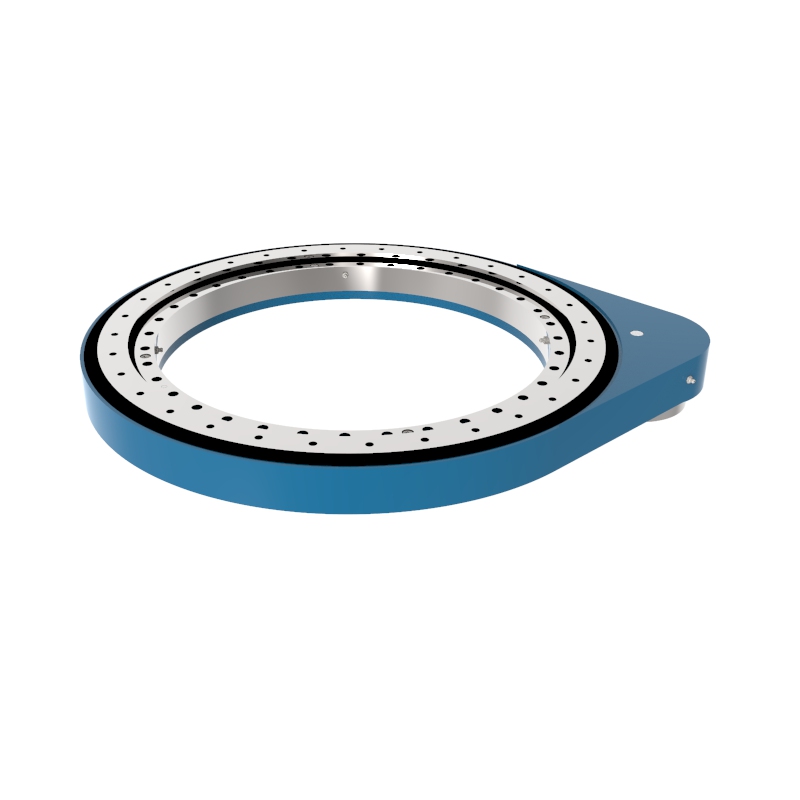
A slew drive is a ready-to-install unit consisting of a ball or roller slewing ring bearing, drive gear, housing, and possibly a motor. It is designed to handle radial, axial, and moment loads, providing rotational motion and power transmission in a compact module. Slew drives are used to control rotational movement with precision and can support heavy loads while maintaining stability.
Lightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0229
SP-I 0229 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery, especially in the occasions that require high precision and high speed.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 1091
The SP-I 1091 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery—particularly in applications requiring high precision, high torque, and reliable speed control.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0841
The SP-I 0841 slewing drive is a robust and compact spur gear slewing solution, engineered for applications requiring precise, stable rotary motion under high load and speed conditions.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0741
SP-I 0741 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery, especially in the occasions that require high precision and high speed.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0641
SP-I 0641 is a compact and lightweight spur gear slewing drive engineered for high-precision rotary motion under dynamic and static load conditions.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0541
The SP-I 0541 is a lightweight external gear slewing drive designed for high-load, high-speed rotary applications. Featuring an integrated slewing bearing and a 10.4:1 gear reduction ratio, this model delivers reliable torque transmission and excellent structural rigidity.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0411
SP-I 0411 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery, especially in the occasions that require high precision and high speed.
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0311
SP-I 0311 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery, especially in the occasions that require high precision and high speed.
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0311
SP-M 0311 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wide
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0411
SP-M 0411 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wide
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0541
SP-M 0541 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wide
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0641
SP-M 0641 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wide
Read More Get A Quote
Types of Slew Drive
Slew drives are primarily categorized based on the type of gears and motors used:
Worm Gear Slew Drives:
These use a worm (a type of gear resembling a screw) to engage with a wheel, providing high torque at low speeds. They are inherently self-locking, making them ideal for applications requiring load holding.
Spur Gear Slew Drives:
These involve spur gears, which are straight-toothed gears. They offer high efficiency and are suitable for applications requiring high speed and lower torque compared to worm gear drives.
Helical Gear Slew Drives:
Similar to spur gears but with angled teeth, helical gears engage more gradually, offering smoother and quieter operation. They are used where noise reduction is critical.
Bevel Gear Slew Drives:
These drives use bevel gears that allow transmission of power between axes that are not parallel. They are typically used in applications requiring the transfer of motion at an angle.
Features of Slew Drive
High Load Capacity: Designed to support heavy axial, radial, and moment loads.
Compact Design: Integrates bearings and gears into a single unit, saving space and simplifying installation.
Precision: Provides accurate control of rotational movement, crucial for applications requiring precise positioning.
Versatility: Available in various configurations to suit different applications and load requirements.
Ease of Maintenance: Typically designed for long life with minimal maintenance requirements.
Customizability: Can be tailored with different motors, encoders, and other modifications to meet specific requirements.
Applications of Slew Drive
Slew drives are used in a wide range of applications across various industries:
Solar Power Systems: For tracking the sun in photovoltaic and concentrated solar power systems.
Wind Turbines: Used in the yaw and pitch adjustment mechanisms.
Cranes and Manlifts: To achieve precise positioning of the boom and basket.
Satellite and Communication Dishes: For accurate positioning to ensure optimal signal reception.
Construction Equipment: In excavators, backhoes, and other heavy machinery for rotation and handling.
Industrial Turntables: To rotate stages, platforms, or heavy loads smoothly.
How to Select Slew Drive?
Selecting the right slew drive involves several considerations:
Load Capacity: Evaluate the maximum loads (axial, radial, and moment) the drive will need to handle.
Operational Speed: Consider the required operational speed and match it with the appropriate gear type.
Precision Requirements: Determine the precision level needed for the application, especially in terms of rotational accuracy and backlash.
Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental conditions such as temperature, moisture, dust, and potential corrosive elements the drive will be exposed to.
Integration Needs: Ensure the slew drive can be integrated into the existing system with appropriate mounting and connection interfaces.
Power Source: Decide on the type of motor or manual operation required based on the application's power availability and control needs.
Budget and Cost-Effectiveness: Balance the performance requirements with the budget, considering not only initial cost but also maintenance and operational costs.