The Engineering Marvel Powering Heavy-Duty Rotation: Unpacking Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearings
What is a Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing?
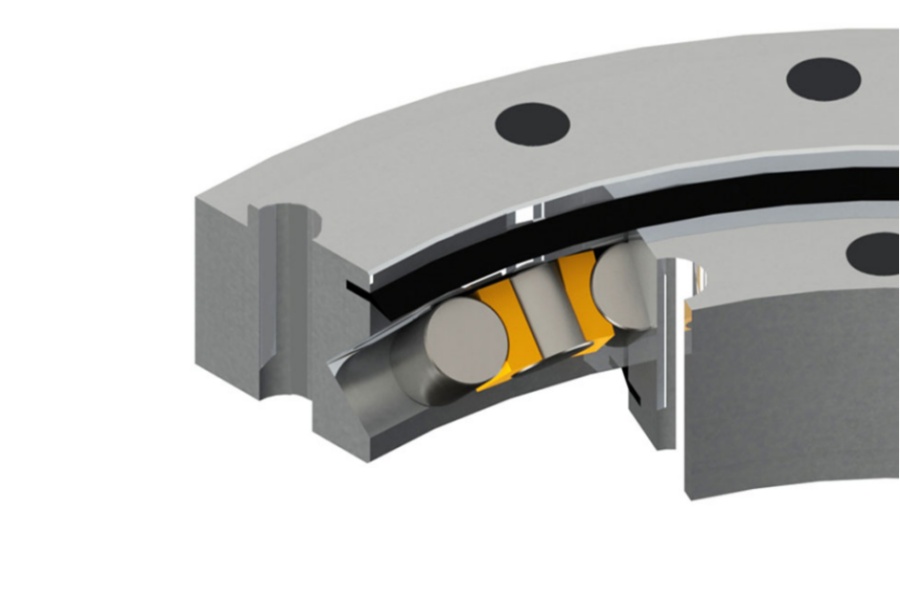
A Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing (often abbreviated as CRB or XRB) represents a pinnacle of slewing bearing design for applications demanding extreme precision and stiffness. Unlike conventional ball slewing bearings or single-row roller bearings, its unique construction features cylindrical rollers arranged in a crisscross pattern (typically at 90 degrees) between two robust rings – an inner ring and an outer ring. This specific arrangement is fundamental to its outstanding performance characteristics. These bearings are engineered as a single, compact unit, eliminating the need for complex multi-bearing setups. The rollers are meticulously guided by precision-machined raceways on both rings and often separated by spacers or cages to maintain optimal spacing and prevent skewing. This intricate design results in a bearing with an exceptionally small cross-section relative to its load capacity and rigidity.

How Does a Crossed Roller Bearing Work?
The magic of the crossed roller bearing lies entirely in its crossed roller arrangement. Imagine cylindrical rollers placed alternately at right angles to each other within the bearing's raceway. One set of rollers is oriented to primarily handle radial loads, while the adjacent set, crossed over them, is oriented to primarily handle axial (thrust) loads. Crucially, due to the line contact of cylindrical rollers and the near-perpendicular arrangement, every single roller effectively contributes to resisting tilting moments. As rotational force is applied to one ring relative to the other, the rollers roll along their respective precision-ground raceways. Because the rollers are crossed, the bearing inherently provides support against loads coming from any direction (radial, axial, or combinations thereof) without needing separate bearing assemblies. The line contact between the rollers and the raceways provides an enormous contact area compared to ball bearings, translating directly into higher load capacity and rigidity. The rolling motion ensures smooth, low-friction rotation with minimal elastic deformation under load.
High Rigidity Slewing Bearing: The Core Advantage
High rigidity is arguably the most critical attribute defining the superiority of crossed cylindrical roller slewing bearings, especially in precision applications. Rigidity refers to the bearing's resistance to elastic deformation (deflection) under applied loads. Why is this so important? Excessive deflection leads directly to:
Loss of Precision: In machine tools, robotics, or medical imaging equipment, even minute deflections can cause significant positioning errors, degrading accuracy and repeatability.
Vibration and Chatter: Lack of stiffness allows vibrations to propagate through the structure, harming surface finish in machining, causing instability in optical systems, or leading to premature fatigue.
Reduced System Performance: Deflection absorbs energy, reducing the efficiency of force transmission and potentially impacting the dynamic response of the entire system.
The crossed roller design achieves exceptional rigidity through two primary mechanisms:
Line Contact: Cylindrical rollers provide significantly more contact area with the raceways than ball bearings (point contact). This larger contact area distributes the load over a broader surface, drastically reducing contact stress and thus, deformation.
Optimized Load Path: The crossed arrangement creates a very short and direct load path from the point of application through the rollers to the supporting structure. This minimizes the leverage effect that causes bending in structures with longer load paths, characteristic of some other bearing configurations. The result is minimal elastic deformation under heavy loads and moments.
Characteristics of Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearings
The unique crossed roller design imparts a distinct set of performance characteristics that make these bearings indispensable for demanding applications:
Exceptional Rigidity: As discussed, minimal elastic deformation under load is paramount for precision.
High Rotational Accuracy: Precision-ground raceways and rollers, combined with the inherent stability of the design, enable extremely smooth running and minimal runout (deviation from perfect circular motion).
Compact Design: Achieves high load capacity and rigidity within a remarkably small axial and radial envelope, saving valuable space in machine design.
High Load Capacity: Handles very high radial loads, axial loads, and tilting moments simultaneously due to the optimized roller contact and arrangement.
Smooth Operation: Low friction torque and consistent rolling characteristics ensure smooth, precise rotation.
Simplified Mounting: Provided as a single, pre-assembled unit with mounting holes, significantly simplifying installation and alignment compared to assembling multiple bearings.
Reduced Sliding Friction: Primarily relies on rolling friction, leading to lower heat generation and potentially longer life compared to designs relying on sliding elements.
High Stiffness-to-Size Ratio: Offers an unparalleled combination of rigidity and compactness
Applications of Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearings
The unique blend of compactness, high rigidity, precision, and load capacity makes crossed roller bearings the preferred solution across numerous high-performance industries:
Robotics: Critical in robot joints (especially articulated arms), rotary tables, and gearing systems where precision positioning, rigidity, and compactness are non-negotiable.
Machine Tools: Found in rotary tables, indexing heads, swivel heads, and tilting spindles for CNC machining centers, grinders, and milling machines, demanding micron-level accuracy and vibration resistance.
Medical Equipment: Essential in CT scanners, MRI machines, radiotherapy devices (LINACs), surgical robots, and patient positioning systems requiring smooth, precise, and reliable motion.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Used in wafer handling robots, steppers, inspection equipment, and lithography stages where nanometer-level precision and stability are paramount.
Industrial Automation: Integral to rotary indexing tables, automated assembly systems, precision welding turntables, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs).
Optical and Imaging Systems: Support high-precision rotary stages for telescopes, satellite tracking systems, laser cutting heads, and high-end cameras requiring stability and minimal vibration.
Aerospace and Defense: Employed in radar antennae platforms, gun turrets, missile guidance systems, and flight simulators where reliability and performance under demanding conditions are critical.
Material Handling: Used in specialized cranes, stacker-reclaimers, and heavy-duty positioning equipment requiring high moment capacity in compact spaces.
Test and Measurement Equipment: Vital for high-accuracy rotary positioning in calibration devices and testing rigs.
Factors Influencing Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing Price
The cost of a crossed roller slewing bearing is significantly higher than standard ball bearings and reflects its complexity, precision, and performance. Key factors include:
Size and Dimensions: Larger diameter bearings naturally require more material and complex manufacturing, increasing cost substantially.
Load Capacity and Rigidity Requirements: Bearings engineered for higher loads, moments, and specific rigidity targets involve more robust designs, potentially larger rollers, optimized heat treatment, and stricter quality control.
Precision Grade: The required level of rotational accuracy (runout), smoothness, and preload significantly impacts machining tolerances, roller sorting, assembly procedures, and inspection rigor. Ultra-high precision bearings command premium prices.
Material Selection: Standard bearings use high-carbon chromium bearing steel. Applications requiring higher corrosion resistance (e.g., medical, semiconductor, marine) necessitate stainless steel (AISI 440C, Cronidur 30, etc.) or specialized coatings, increasing material and processing costs.
Customization: Standard catalogue bearings are most economical. Modifications like special mounting hole patterns, flanges, integrated gears, custom seals, specific lubrication systems, or unique bore/OD dimensions add engineering and manufacturing costs.
Sealing: Standard lip seals are common. Demanding environments requiring high IP ratings, specific chemical resistance, or ultra-cleanliness (labyrinth seals, special compounds) add cost.
Lubrication: Standard grease filling is typical. Requirements for specific high-performance greases, lifetime lubrication, or centralized lubrication ports add cost.
Quantity: Unit price generally decreases with higher order quantities due to amortized setup costs and more efficient production runs.
Brand Reputation and Quality Certification: Bearings from manufacturers with established reputations for quality, reliability, and rigorous quality control systems (ISO certifications, industry-specific standards) often command higher prices. Investment in R&D and advanced manufacturing capabilities is reflected in the cost.
Geographic Origin: Manufacturing location and associated labor costs, logistics, and import duties can influence final pricing.
Suppliers of Crossed Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing
Selecting the right supplier for crossed cylindrical roller slewing bearings is critical, as performance, longevity, and reliability directly impact the success of your application. Look for suppliers with demonstrable expertise in precision bearing manufacturing. LYRADRIVE stands out as a premier manufacturer and supplier in this specialized field.
LYRADRIVE distinguishes itself through:
Deep Technical Expertise: Extensive engineering knowledge to understand complex application requirements and provide optimal bearing solutions, not just standard products.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities: Investment in state-of-the-art machining, grinding, heat treatment, and quality control equipment ensures consistent production of high-precision bearings.
Stringent Quality Control: Rigorous inspection protocols at every stage (material incoming, machining, grinding, assembly, final testing) guarantee adherence to tight tolerances and performance specifications. Compliance with international quality standards (ISO 9001, etc.) is fundamental.
Material Mastery: Expertise in selecting and processing appropriate bearing steels and stainless steels for diverse operational environments and performance demands.
Customization Prowess: Proven ability to engineer and manufacture bespoke crossed roller bearings tailored to unique size, load, rigidity, sealing, mounting, or integration requirements.
Application Focus: Experience across critical industries like robotics, machine tools, medical, and automation provides valuable insight into solving real-world challenges.
Global Support: Offering comprehensive technical support, reliable logistics, and responsive customer service from inquiry through installation and maintenance.
When performance, precision, and reliability cannot be compromised, partnering with a specialized supplier like LYRADRIVE ensures access to the advanced engineering, manufacturing excellence, and dedicated support required for your most demanding rotational challenges. Their focus on pushing the boundaries of crossed roller bearing technology makes them a trusted resource for engineers designing the next generation of high-performance machinery.



