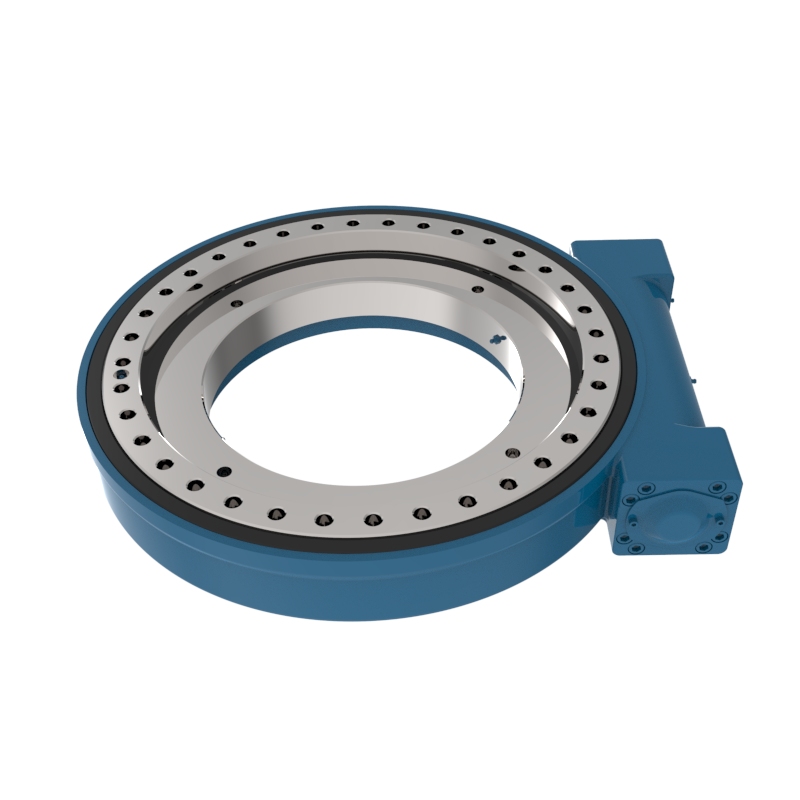
What is the slewing drive used for?
A slewing drive is a self-contained module that integrates a slewing ring bearing with a drive mechanism, typically a worm gear, to provide controlled rotational motion. This device allows for both axial and radial forces and moment loads, making it highly effective for applications requiring precise and reliable movement under load.

Types of Slewing Drive
Slewing drives come in various types, mainly differentiated by their design and the specific applications they serve:
Worm Gear Slewing Drives:
Single Worm Drive: Commonly used, it offers simple and effective rotational motion control with self-locking capability, which prevents reverse rotation under load.
Dual Worm Drive: Provides higher precision and greater torque handling capacity. It is better at reducing backlash and offers improved load distribution.
Spur Gear Slewing Drives:
Less common than worm gear drives, spur gear versions offer higher efficiency and speed capabilities but lack the inherent self-locking feature of worm gears.
Vertical and Horizontal Mounting:
Slewing drives can be mounted vertically or horizontally, depending on the application needs. The orientation affects the load distribution and operational efficiency.
Applications of Slewing Drive
Slewing drives are used in a variety of applications, particularly where precision and reliability are crucial:
Solar Trackers: They are extensively used in solar power systems to rotate solar panels towards the sun throughout the day, maximizing energy absorption.
Wind Turbines: Adjusting the position of the turbine blades to optimize wind capture and protect the blades from high winds.
Satellite and Radar Dishes: Precise positioning of communication equipment to ensure optimal alignment and signal reception.
Cranes and Manlifts: Providing rotational capability and stability in lifting operations.
Industrial Machinery: Applications include turntables, assembly jigs, and other machinery requiring rotational movement.
How to Select a Slewing Drive?
Selecting the right slewing drive involves several key considerations:
Load Calculation:
Understand the axial, radial, and moment loads the drive must support. This will help determine the size and type of slewing drive needed.
Operational Requirements:
Consider factors like the speed of operation, precision needed, and degree of backlash acceptable.
Environmental Conditions:
Account for operating conditions such as temperature, weather exposure, and potential contaminants which might necessitate specific sealing or protective measures.
Mounting Configuration:
Decide on the mounting orientation (vertical or horizontal) based on the application's spatial and operational requirements.
Power Source:
Determine the type of motor or actuator (electric, hydraulic, etc.) that will be used based on availability and suitability for the environment and workload.
Maintenance and Lifespan:
Consider how often maintenance can be performed, and select a drive that offers a balance between durability and serviceability.
By carefully evaluating these factors against the requirements of your specific application, you can choose a slewing drive that will perform effectively and reliably. Manufacturers often provide detailed product specifications and can offer guidance based on their experience with similar applications, which can be an invaluable resource in the selection process.
Slewing Drive Manufacturer
Lyra Drive is a professional and one-stop slewing bearing, slewing drive, gear rings and other machinery parts manufacturer in China. If you are looking for high quality and reliable slewing drive, feel free to contact us.


