The Life-or-Death Battle for Steel Joints: How Heavy-Duty Slewing Bearings Bear Immense Loads Without Cracking
What is a Heavy load slewing bearing?
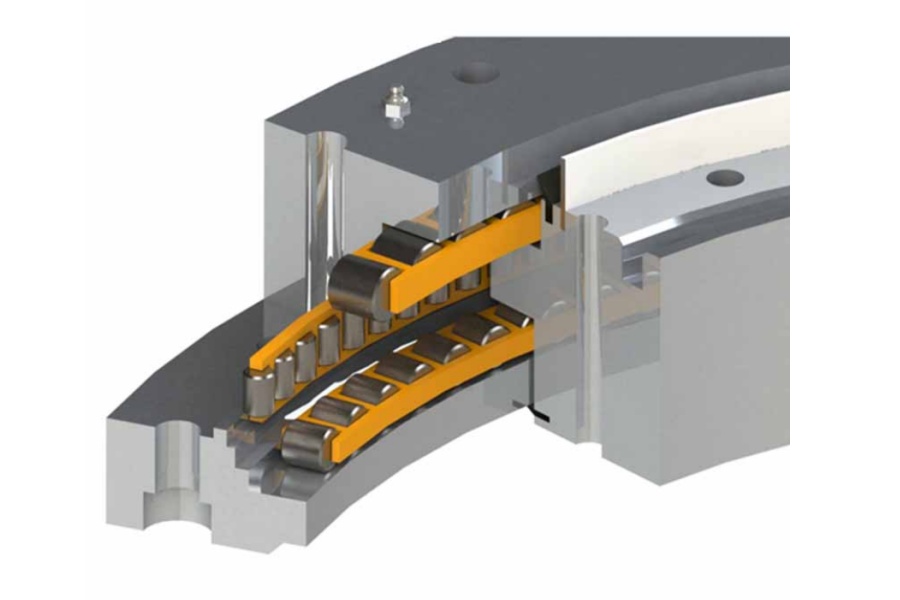
A Heavy load slewing bearing is far from just an enlarged version of a standard bearing. It is an engineering masterpiece born to withstand extreme combined loads, integrating missions of ultra-strong load-bearing, precision rotation, and long-term service. Its defining features are unmistakable:
Unrivaled Strength: Designed to endure axial loads (vertical pressure), radial loads (horizontal thrust), and massive overturning moments (anti-tipping force) reaching thousands of tons—tens or even hundreds of times the limits of conventional bearings.
Colossal Scale: Diameters typically measured in meters, ranging from one to over ten meters, with robust, solid structures and substantial material use.
Integrated Functionality: Combines internal or external gear rings, multi-layered sealing systems, lubrication channels, and even sensor interfaces into one unit—serving as both a bearing and a transmission component.
Precision Demands: Must ensure smooth rotation, precise positioning, and minimal friction even under crushing pressure, demanding near-perfect manufacturing accuracy.
Customization is King: Almost always tailored to the unique operating conditions, space constraints, and performance requirements of host machinery, rarely off-the-shelf.
Its core structure includes an inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements (balls or rollers), and a cage. The raceways on the inner and outer rings undergo specialized hardening treatments (like deep carburizing and quenching) to form nearly indestructible load-bearing surfaces.

How to Prevent Slewing Bearing Cracking? Guarding the Life-or-Death Line of Industrial Joints
Cracking is the most fatal and costly failure mode for Heavy load slewing bearings. Preventing it is a battle fought across the entire lifecycle—design, manufacturing, installation, and operation:
Design Source: Precision Calculation & Simulation
Load Spectrum Analysis: Precisely calculate the combined axial, radial, and overturning moment forces under all operating scenarios, including shock loads. Eliminate "close enough" estimates.
Material Science: Use high-toughness, high-strength alloy steels (e.g., 42CrMo, 50Mn), strictly control steel purity and homogeneity, and avoid internal defects becoming crack origins.
Structural Optimization: Raceway profiles, transition fillet radii, and bolt hole distribution must be optimized via Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to eliminate stress concentration points. Triple-row roller designs excel in resisting overturning and dispersing stress.
Heat Treatment Simulation: Predict temperature fields and stress fields during processes like carburizing and quenching for large workpieces; optimize processes to minimize residual stress.
Manufacturing Core: Zero-Compromise Processes
Forging Quality: Large forgings must be defect-free and dense, with rational grain flow direction.
Precision Heat Treatment Control: Deep carburizing and quenching/induction hardening are critical. Strictly control case depth, hardness gradient, and core toughness. Use press quenching to reduce distortion and thermal stress. Ensure sufficient tempering to relieve stress.
Precision Machining: Achieve micron-level accuracy in raceway grinding and gear tooth machining. Avoid surface defects like tool marks. Strictly control geometric tolerances (roundness, flatness).
Comprehensive Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Layer-by-layer inspection—after forging, rough machining, finish machining, and heat treatment. Ultrasonic Testing (UT) for internal defects; Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)/Penetrant Testing (PT) for surface cracks. 100% inspection of critical areas.
Installation Lifeline: Precision and Protocol
Foundation Rigidity: Mounting surfaces (base) must have extreme rigidity and flatness. Any "soft foot" or distortion causes localized stress spikes, leading to premature cracking. On-site machining may be necessary. Bolt Pre-tensioning: Use hydraulic tensioners or torque wrenches to apply step-by-step, cross-patterned, uniform bolt pre-tension strictly per design. Insufficient or excessive preload is disastrous. Regularly re-tighten.
Precise Alignment: Ensure proper meshing between inner/outer rings and drive gears to avoid extra stress. Use laser alignment tools.
Clean Lubrication: Maintain absolute cleanliness during installation. Use specified initial grease to fully fill the raceways.
Operation & Maintenance: Monitoring and Intervention
Strictly Avoid Overload: A direct cause of overload cracking. Strictly adhere to equipment load charts.
Lubrication Lifeline: Replenish specified grease regularly, quantitatively, and qualitatively. Degraded grease or dry friction causes sharp temperature rises, leading to material annealing, plummeting strength, and crack formation. Check seal effectiveness.
Condition Monitoring: Integrate temperature and vibration sensors for real-time monitoring. Abnormal temperature rises or vibrations are early signs of crack development. Conduct regular vibration analysis and grease ferrography analysis.
Regular Inspections: Professionals should periodically check bolt preload, seal condition, unusual noises, and abnormal wear debris.
Overload Protection: Equipment must have reliable safety devices like moment limiters.
Industrial Slewing Bearings: The Steel Heart Driving Foundational Industries
Beyond the "heavy-duty" category, industrial slewing bearings are the invisible power sources on factory production lines:
Steel Titans: Tilt bearings for steelmaking converters, ladle turret bearings for continuous casters, enduring molten steel impact and high-temperature radiation.
Cement Backbone: Giant support roller bearings for cement kilns, supporting thousand-ton cylinders rotating slowly amid dust and heat.
Mining Lifelines: Bearings for ball mills and rotary kiln feed ends, operating persistently amid vibration and ore dust.
Chemical Core: Slewing supports for large reactors and agitators, requiring corrosion and media resistance.
Waste-to-Energy: Drive bearings for rotating grates in waste incinerators, battling high temperatures and corrosion.
Though bearing slightly less load than mining behemoths, these slewing bearings demand extremely high reliability, environmental resistance (heat, dust, corrosion), and continuous service life—key to ensuring 24/7 operation of industrial production lines.
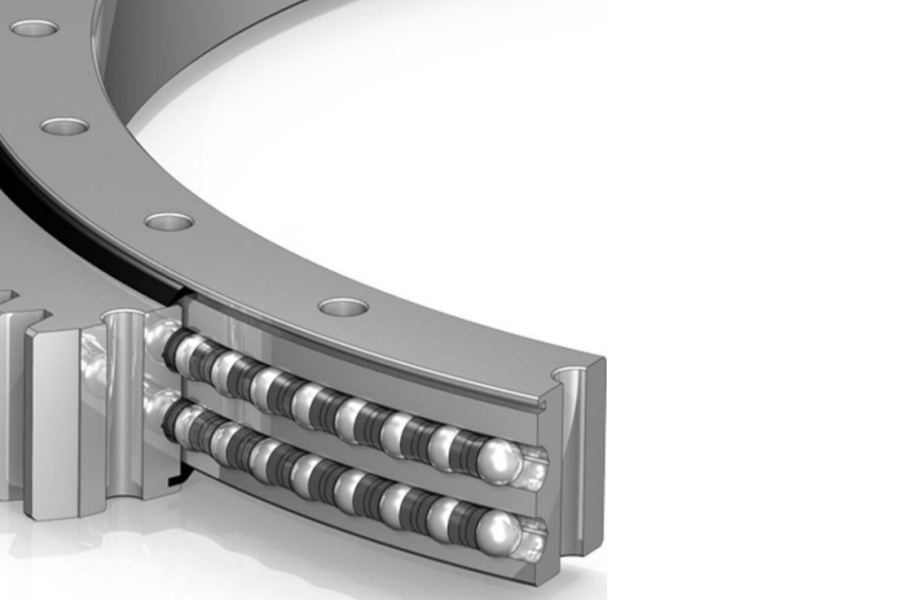

Low-Temperature Slewing Bearings: Extreme Warriors Conquering Frozen Battlefields
When industrial giants venture into polar regions, high-altitude permafrost, or LNG applications, conventional bearings risk fatal brittle fracture due to material cold-embrittlement. Low-temperature slewing bearings are built for extreme cold, from -40°C to -60°C (or lower):
Material Revolution: Core use of high-toughness, low-temperature specialty alloy steels (e.g., ASTM A148 Gr. 80-50), ensuring exceptional impact toughness even in deep cold, resisting brittle fracture.
Low-Temperature Toughness Treatment: Special heat treatment processes (quenching + cryogenic treatment + tempering) to maximize steel toughness at low temperatures.
Cold Assembly Technology: Strictly control clearance tolerances at room temperature, accounting for steel shrinkage coefficients in extreme cold to prevent "seizing" or excessive gaps.
Low-Temperature Lubrication: Special synthetic low-temperature greases maintain good fluidity even at -50°C, avoiding solidification failure. Seal materials must also withstand cold.
Battlefield Applications: Cranes on polar research vessels, high-altitude mining equipment, LNG ship loading arms, large radar stations in frigid zones, permafrost construction machinery (e.g., rotary drilling rigs).
Heavy load slewing bearings: The Industrial Cornerstone Lifting a Thousand Industries
Their presence spans every heavy-load rotation point in modern industry:
Energy Titans: Wind power (yaw, pitch), hydropower gate hoists.
Mining Masters: Giant hydraulic excavators, electric shovels, dump trucks, stacker-reclaimers.
Port Arteries: Ship-to-shore cranes, rubber-tired gantry cranes (RTGs), large portal cranes.
Construction Backbone: Tower cranes, crawler cranes, tunnel boring machine (TBM) cutterhead drives.
Metallurgical Core: Steelmaking converters, ladle turrets, steel rolling equipment.
Marine Heavyweights: Shipboard cranes, offshore platform cranes, naval gun turrets.
Defense Sentinels: Radar antenna pedestals, missile launcher turntables.
Environmental Warriors: Grabbing cranes for waste, drive bearings for rotary grates in incinerators.
The Extraordinary Traits of Heavy load slewing bearings: Steel Body, Intelligent Heart
Core attributes enabling their immense responsibilities:
Titanic Strength: Peerless capacity for combined loads (axial + radial + overturning moment).
Rock-Solid Stability: Extreme rigidity under deformation, ensuring rotational accuracy and smoothness.
Enduring Toughness: Premium alloy steel + deep hardening + precision manufacturing → resistance to wear, fatigue, impact → decades-long lifespan.
Silky-Smooth Rotation: Optimized raceway geometry and precision machining enable low-friction, low-energy operation even under heavy loads.
Fearless in Adversity: Multi-layered sealing barriers + long-life lubrication → defense against dust, moisture, salt spray.
Integrated Intelligence: Gear rings and sensor interfaces simplify host machine design.
Perceptive Vision (Trend): Built-in sensing ushers in the era of predictive maintenance.
The Price Code of Heavy load slewing bearings: The Complex Equation Behind Value
Their premium price is determined by multiple intertwined dimensions:
Steel Foundation: Cost of specialty alloy steels (42CrMo, 50Mn, etc.) is massive. Size/weight exponentially increases cost.
Craftsmanship Precision:
Structural Complexity: Triple-row roller > double-row ball > single-row ball; integrated gears significantly add cost.
Manufacturing Accuracy: Large-scale precision CNC machining, micron-level grinding, complex heat treatment (carburizing/quenching) require expensive equipment, long cycles, and face yield challenges.
The Soul of Heat Treatment: Deep carburizing/quenching for large components is energy-intensive and hard to control, adding significant cost.
Performance Pinnacle:
Load & Lifespan: Higher static/dynamic loads, overturning resistance, longer design life (e.g., 20+ years for wind) demand stricter material and process requirements.
Special Demands: Low-temperature toughness, ultra-high corrosion resistance, explosion-proof certification (e.g., ATEX), classification society approval (DNV/GL/ABS) incur extra costs.
Protection Shield: High-performance seals, centralized lubrication systems, special coatings, sensor integration all add cost.
Customization Level: Fully custom designs far exceed standard models or minor modifications.
Brand Equity: Premiums exist for top brands like Rothe Erde, Schaeffler, TMB, ZWZ.
Logistics Challenge: Special transport and lifting costs for oversized, super-heavy parts are staggering.
Guarding Rotation is Guarding Industrial Lifeblood
Heavy load slewing bearings are the fusion of strength and intelligence in steel—the rotating lifeline upon which modern heavy industry relies. Understanding their essence, mastering anti-cracking strategies, clarifying their applications in harsh industrial and cryogenic environments, and deciphering their value composition are crucial for equipment manufacturers, end-users, and maintainers. Every act of scientific selection, precise installation, standardized operation, and meticulous maintenance of a Heavy load slewing bearing is a solid guarantee for vast industrial assets and sustained productivity. As we advance toward larger scales, higher efficiency, and more extreme environments, the technological evolution of Heavy load slewing bearings is endless. They will continue to drive the mighty progress of human industrial civilization with their steel bodies. When a ten-thousand-ton boom rotates steadily in icy winds, when a giant shovel excavates precisely in a kilometer-deep mine—that is the Heavy load slewing bearing, this silent industrial giant, declaring victory under immense pressure.
Supplier of Heavy load slewing bearing
LYRA Drive is a professional slewing bearings ,slew drive and gears manufacturer provides customized slew bearing, drive and gears.For application-specific engineering solutions, contact LYRA to discuss technical specifications and implementation strategies.



