Slewing Bearings in Filling Machines
What is Slewing Bearing
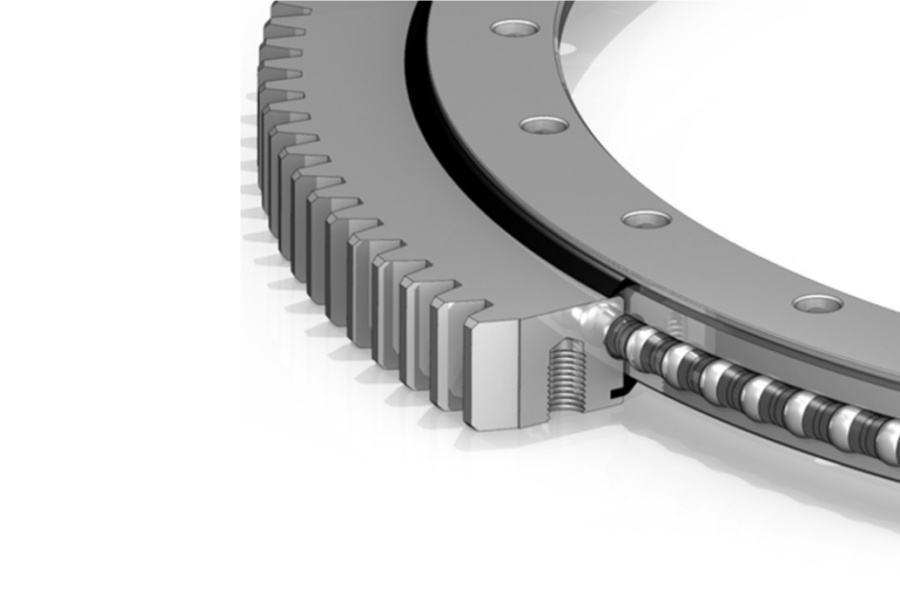
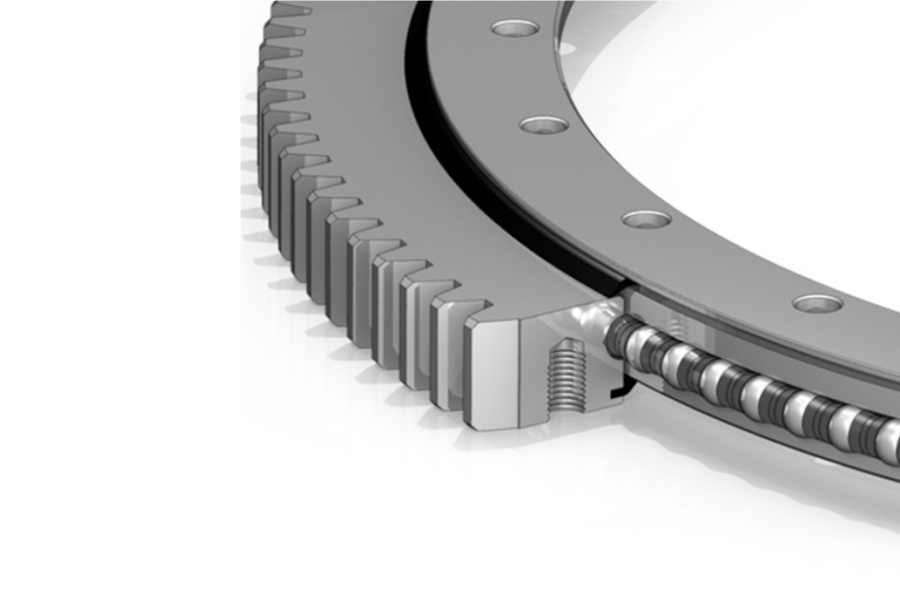
Slewing Bearing is a highly engineered rotary bearing designed to manage complex combinations of axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously, enabling smooth, controlled rotational movement in demanding industrial machinery. Comprising inner and outer rings housing rolling elements (balls or rollers), they are typically sealed against contaminants. Distinct from standard bearings, slewing bearings support substantial tilting moments and feature large diameters, making them indispensable in applications like cranes, excavators, wind turbines, and automated production lines such as fillers. Constructed from hardened steel or specialized alloys, their robust design ensures exceptional durability and longevity even in harsh operating environments. By significantly reducing friction and wear in rotational systems, slewing bearings enhance operational efficiency and extend equipment lifespan, underpinning stability and precision across diverse industrial sectors.
Role of Slewing Bearings in Filling Machines
Slewing bearings are fundamental components within filling machines, driving critical rotational functions that maximize production speed, accuracy, and versatility. Their specific roles include:
Rotating Filling Heads: Enabling filling heads equipped with multiple nozzles to rotate, precisely positioning each nozzle over containers on a moving platform for rapid, uniform filling.
Position Adjustment: Facilitating fine adjustments to the position and alignment of filling components, allowing quick adaptation to different container sizes or shapes, minimizing changeover downtime.
Product Distribution: Rotating complex distribution systems to accurately dispense different products into specific containers during multi-product filling processes.
Conversion Mechanisms: Allowing smooth transitions between different product types or container formats within the machine, enhancing automation and reducing manual intervention.
Capping and Sealing: Rotating capping or sealing mechanisms to apply closures accurately and reliably, ensuring packaging integrity after filling.
Selecting the optimal slewing bearing for a filling machine requires careful consideration of load capacity (handling container weights), diameter (machine fit), installation requirements, precision (for accurate positioning), and resilience to environmental factors like liquids, cleaning agents, dust, and temperature variations. Collaboration between engineering teams and bearing specialists is crucial to ensure the chosen bearing delivers the required performance, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
Key Characteristics of Slewing Bearings
Slewing bearings possess defining characteristics essential for their demanding roles:
High Load Capacity: Engineered to support immense weights and dynamic forces (axial, radial, moment) without deformation, critical for heavy industrial use.
Low Friction Operation: Optimized rolling elements and lubrication systems minimize friction, reducing energy consumption and heat generation during rotation.
Exceptional Durability: Manufactured from hardened steel or corrosion-resistant alloys and featuring robust seals, they withstand abrasive, corrosive, or washdown environments common in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical filling.
High Precision: Precision engineering ensures minimal backlash and high positional accuracy, enabling exact movements required in automated filling sequences.
Modularity and Customization: Offered in various sizes and configurations, often customizable with integrated gear teeth, specific mounting options (bolt patterns, flanges), or special seals to fit diverse machinery layouts.
Compact Design: Efficiently handles multi-directional loads within a relatively compact space envelope.
Advanced Features: Modern variants may include integrated sensors for real-time monitoring of load, temperature, or vibration.
Low Maintenance: Their robust construction and sealing contribute to long service intervals and reduced operational costs over time, resisting wear, vibration, and environmental stressors.
Applications Beyond Filling Machines
While vital to filling machines, slewing bearings enable rotation across numerous industries:
Construction Machinery: Essential for crane booms, excavator turntables, and access platforms, handling extreme loads and harsh site conditions.
Renewable Energy: The cornerstone of wind turbine nacelles, allowing blades to rotate and align optimally with wind direction.
Material Handling: Powering robotic arms, conveyor turntables, stacker-reclaimers, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for precise positioning and movement.
Aerospace & Defense: Enabling rotation in radar systems, satellite communication dishes, missile launchers, and aircraft cargo loaders.
Medical Equipment: Used in adjustable imaging devices (CT/MRI scanners) and surgical robotics for precise movement.
Marine & Offshore: Critical for ship cranes, deck machinery, davits, and offshore crane pedestals, demanding high corrosion resistance.
Mining & Heavy Industry: Found in tunnel boring machines, large draglines, and processing equipment under severe loads and contamination.
This versatility stems from their unique ability to manage combined loads and provide reliable rotation in high-stress, high-precision environments.
Factors Influencing Slewing Bearing Price
The cost of a slewing bearing is determined by several key factors:
Material Composition: Bearings made from premium alloys (e.g., high-grade chromium steel, stainless steel for corrosion resistance) or requiring specialized heat treatment command higher prices due to enhanced durability and performance.
Size and Complexity: Larger diameter bearings require significantly more raw material and machining time. Custom designs, non-standard dimensions, or complex geometries increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Load Capacity and Ratings: Bearings engineered for higher axial, radial, and moment load capacities demand more robust design, thicker sections, advanced materials, and rigorous testing, escalating the price.
Precision Requirements: Tighter tolerances (e.g., minimal runout, reduced backlash) necessitate specialized, high-precision machining processes and extensive quality control, adding to the cost.
Environmental Protection: Higher IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, specialized seals (e.g., for food-grade or high-pressure washdown), or corrosion-resistant coatings increase manufacturing costs.
Customization: Integrated features like gear teeth (internal or external), custom bolt patterns, specific lubrication systems, sensor mounts, or special flange designs require additional engineering and production steps.
Volume: Economies of scale apply; larger order quantities typically reduce the per-unit cost.
Brand and Supplier: Reputable manufacturers with proven quality control and R&D investment often command premium pricing. Supplier markups and distribution channels also influence the final cost.
Market Dynamics: Global factors such as raw material (steel) costs, energy prices, tariffs, import/export duties, and shipping logistics cause price fluctuations based on demand and regional supply chains.
Supplier of Slewing Bearing
LYRADRIVE is a prominent global supplier of high-performance slewing bearings engineered for reliability in demanding industrial applications, including filling machines. They offer an extensive product portfolio featuring bearings constructed from advanced materials with precision manufacturing, ensuring robust load capacity, exceptional durability, and smooth operation. LYRADRIVE emphasizes customization, providing solutions tailored to specific machine requirements such as size, sealing, gearing, and mounting configurations. Backed by technical expertise and responsive global support, LYRADRIVE focuses on delivering optimal bearing solutions that enhance equipment efficiency, longevity, and productivity for manufacturers worldwide.



