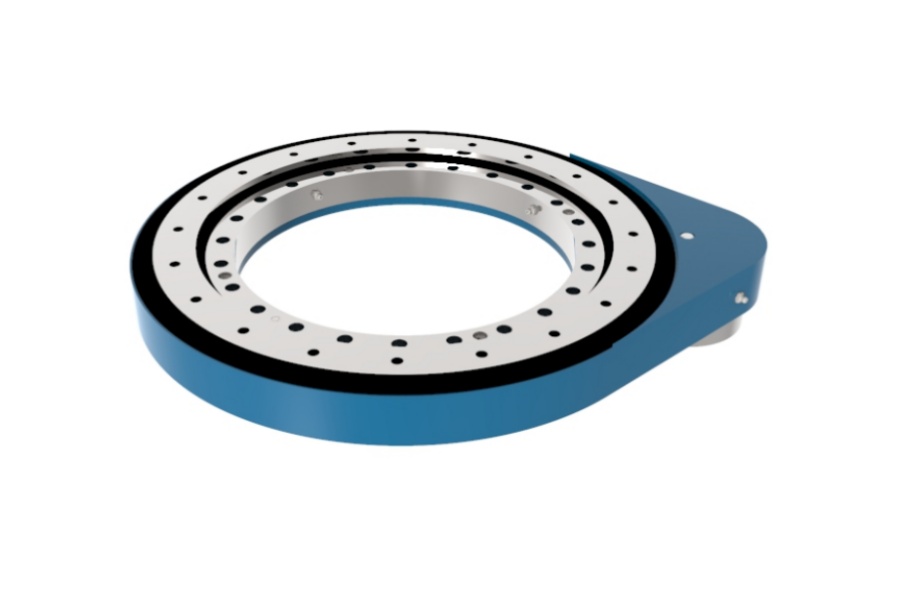
Slew Drive Seals The Critical Role of Oil Seals
What is a Slew Drive
A Slew Drive is an integrated mechanical assembly that combines a slewing ring bearing with a worm gear or other drive mechanism to facilitate controlled rotational movement. This compact system is engineered to transmit high torque from a compact motor source while simultaneously supporting substantial axial, radial, and moment loads. Its design integrates multiple functionalities into a single, self-contained unit, making it a cornerstone component for machinery requiring precise, heavy-duty rotation. The efficiency and service life of a slew drive are profoundly dependent on the integrity of its internal components, which must be protected from wear and environmental damage. This critical protective function is fulfilled by a system of seals, with oil seals being among the most vital, acting as the primary barrier that safeguards the internal workings of the drive.
Oil Seals in Slew Drives
Oil seals, also referred to as shaft seals or rotary seals, are precision components designed to retain lubricating grease or oil within the slew drive's internal cavity and to prevent the ingress of external contaminants such as dirt, dust, water, and grit. In the demanding environment of a slew drive, these seals are subjected to continuous rotational movement, extreme pressures, temperature fluctuations, and potential exposure to harsh elements. Their failure directly leads to lubricant loss, contamination ingress, accelerated wear of the worm gear and gear ring, and ultimately, catastrophic failure of the entire unit. Therefore, the selection of appropriate seal types and materials is a critical engineering decision.
Primary Functions:
The core functions of oil seals in a slew drive are containment and exclusion. Effective containment ensures that the lubricant essential for reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing metal-to-metal contact between the meshing worm and gear ring remains within the system. Simultaneously, exclusion is the process of creating a dynamic barrier that blocks abrasive and corrosive contaminants from entering the drive's precision-machined internal spaces. Any compromise in either function drastically shortens the operational life of the drive.
Common Seal Types:
Slew drives utilize a combination of seal types to achieve optimal protection. Radial Lip Seals are the most common type of oil seal. They consist of a flexible rubber lip that is held in contact with the rotating shaft or housing by a garter spring. This design provides an excellent dynamic seal but is subject to wear over time. PTFE (Teflon) Seals offer superior chemical resistance and can perform across a wider temperature range than elastomeric seals. They are often used in applications involving extreme temperatures or corrosive chemicals. Labyrinth Seals are non-contact seals that create a complex, tortuous path for contaminants to navigate. While they do not provide a perfect seal, they are highly effective at excluding large amounts of coarse contaminants and are often used in conjunction with contact seals in very harsh environments like mining or construction. V-Ring Seals are static seals that are pressed onto a shaft and rotate with it, deflecting contaminants away from the sealing area with a flinging action. They are simple and effective at handling mud and coarse abrasives.
Seal Materials:
The material selection for the sealing element is dictated by the operating environment, temperature, and lubricant type. Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a general-purpose, cost-effective material with good resistance to petroleum-based oils and greases, and a standard temperature range. It is widely used in industrial applications. Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) offers improved temperature resistance and superior mechanical properties compared to standard NBR, making it suitable for more demanding conditions. Fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton) is the premium choice for high-temperature applications and offers excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, oils, and fuels. It is essential in settings like metal processing or near high-heat sources. Polyurethane (PU) is renowned for its exceptional abrasion resistance and toughness, making it ideal for applications with high levels of particulate matter, such as in mining or heavy construction equipment. PTFE provides the highest level of chemical and temperature resistance, though it is typically more expensive.
Failure Modes and Consequences:
Common reasons for seal failure include abrasive wear from harsh contaminants, hardening and cracking due to excessive heat or ozone exposure, lip tearing from improper installation or sharp edges, and chemical degradation from incompatible fluids. A failed seal leads directly to lubricant leakage, which starves the worm gear and bearing raceways of lubrication, causing rapid, excessive wear. Contamination ingress acts as a grinding paste, accelerating abrasive wear on the precision gear teeth and rolling elements, increasing operating backlash, and generating noise and vibration. Ultimately, this results in a loss of precision, a drop in torque capacity, and complete drive seizure.
Key Characteristics of Slew Drives
Slew drives are defined by several key characteristics that make them indispensable in heavy machinery. Their high torque output relative to their compact size is a fundamental feature, enabling them to drive large loads with a small motor. They are uniquely engineered to handle combined loads, meaning they can simultaneously support axial, radial, and moment (tilting) forces, which simplifies structural design for OEMs. The inherent self-locking capability of the worm gear design provides built-in load-holding security, preventing the load from driving the mechanism backwards in the event of drive power loss. Many slew drives are designed for precise positioning and control, with options for low backlash to ensure accuracy in applications like solar tracking or robotics. Finally, their integrated nature combines a bearing, gearbox, and mounting structure into one sealed unit, reducing the number of components an equipment manufacturer needs to source, assemble, and maintain.
Primary Applications of Slew Drives
The robust and versatile nature of slew drives makes them critical components across a vast spectrum of industries. In the renewable energy sector, they are the actuating heart of solar trackers, meticulously adjusting the angle of PV panels to follow the sun's path, thereby maximizing energy generation. The construction and mining industry relies heavily on them to provide the rotation for excavator upper structures, crane booms, concrete pump booms, and drilling equipment. Within wind power, slew drives are used in yaw systems to orient the nacelle into the wind and in pitch systems to adjust blade angle for power control. The aerospace and defense sectors utilize them in radar antenna positioning, missile launch systems, and satellite communication equipment. Other significant applications include material handling (stackers, reclaimers, rotators), industrial automation (heavy-duty robotic turntables, welding positioners), and medical equipment (where precision and reliability are paramount).
Factors Influencing Slew Drive Pricing
The cost of a slew drive is influenced by a multitude of interrelated factors. The raw material cost for major components like the gear ring, worm gear, and housing, whether it is standard carbon steel, high-grade alloy steel, or stainless steel, forms a significant portion of the base cost. The physical size and load capacity of the unit are direct cost drivers; larger drives designed for higher moment loads require more material, larger forgings, and more powerful heat treatment facilities. Performance and precision requirements, such as ultra-low backlash specifications, high positional accuracy, or defined efficiency ratings, necessitate more sophisticated manufacturing techniques, superior quality control, and selective assembly, all adding to the expense. The choice of ancillary components, including the type, quality, and number of seals (standard rubber vs. high-performance PTFE), the grade of internal bearings, and the quality of the lubricant, also impact the final price. Furthermore, any customization, such as special bolt patterns, unique shaft configurations, custom paint, or special seal arrangements for extreme environments, requires additional engineering and manufacturing resources. Finally, order volume plays a crucial role, with mass production for OEMs benefiting from economies of scale that are not available for small-batch or single-unit orders.
Supplier of Slew Drive
For engineers and procurement specialists seeking a reliable source for high-performance slew drives, LYRADRIVE stands as a capable global supplier and manufacturer. The company specializes in the design and production of a wide range of standard and custom slew drives and slewing bearings, engineered to meet rigorous application demands. LYRADRIVE's focus on technical expertise and quality manufacturing ensures that its products are built to deliver reliable service, with a particular emphasis on robust sealing solutions tailored to the operating environment. They offer options in various seal types and materials, including high-performance configurations for the most challenging conditions in mining, marine, and offshore applications. By combining engineering support with a commitment to quality, LYRADRIVE provides effective rotational drive solutions for a diverse international clientele.



