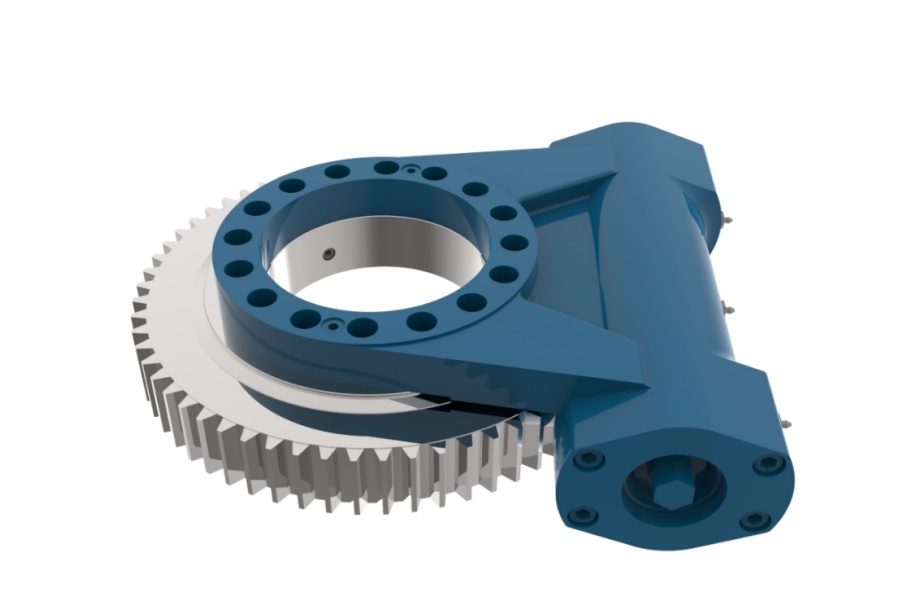
Installation Bolt Arrangement Methods for Slew Drives
What is S Slew Drive?
S Slew Drive represents a highly engineered class of rotational drive systems. At its core, it integrates essential components like a precision worm gear set (comprising a hardened worm shaft and a large diameter worm wheel) and robust bearings (typically crossed roller bearings or large-diameter slewing rings) into a compact, sealed housing. This integrated design delivers exceptional torque transmission capabilities, precise rotational control, and the ability to manage substantial axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously. S Slew Drives are fundamental mechanisms for achieving controlled, high-load rotational movement in a vast array of heavy-duty machinery and precision positioning equipment.
Bolt Arrangement Methods During Slew Drive Installation
The correct layout and tightening of mounting bolts are paramount for the slew drive's performance and lifespan. Adhering to established engineering principles ensures safe and efficient operation:
Simplicity and Symmetry: The mounting interface on the supporting structure should be as simple and flat as possible. The bolt pattern should ideally possess two perpendicular axes of symmetry. Crucially, the bolt group's centroid (center of mass) must align precisely with the centroid of the slew drive's mounting surface to prevent uneven loading and potential distortion.
Optimal Bolt Count & Spacing: Utilize bolt counts conducive to easy machining division during hole drilling, such as 4, 6, 8, or 12 bolts arranged in a circular pattern. This ensures consistent angular spacing.
Handling Loads:
Moment Loads: When the slew drive transmits significant tilting moments, position bolts farther away from the pattern's central axes. This maximizes the effective lever arm, reducing the tensile force required per bolt to counteract the moment.
Radial/Shear Loads: If substantial radial or shear forces are anticipated, orient more bolts along the primary direction of the force. However, limit the number of bolts directly in line with the force to 6-8 to avoid severe uneven load sharing among bolts.
Consistency: All bolts, nuts, and washers within the same mounting set should be identical in size, grade, material, and finish. This simplifies procurement, prevents assembly errors, and ensures uniform preload and performance.
Accessibility: Design the surrounding structure to provide ample clearance for standard tightening tools (wrenches, torque multipliers, hydraulic tensioners). Strictly adhere to recommended minimum wrench clearance dimensions to allow for proper tightening and future maintenance access. Neglecting this can lead to improperly torqued bolts or necessitate costly disassembly later.
Preload Control: Follow the manufacturer's specifications meticulously for bolt tightening torque or tension (preload). Achieving the correct, uniform preload across all bolts is essential for joint integrity and preventing bolt fatigue failure. Use a calibrated torque wrench or, preferably for critical applications, a hydraulic bolt tensioning system applied in a star pattern sequence.
Key Characteristics of S Slew Drives
S Slew Drives distinguish themselves through several vital performance attributes:
Exceptional Load Capacity: Engineered to withstand extreme combinations of axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously, often far exceeding the capabilities of standard gearboxes.
High Torque Density: Delivers immense torque output relative to its compact size and weight, optimizing space utilization in machinery design.
Precision Motion Control: Offers high positioning accuracy, repeatability, and smooth, controlled rotational movement, essential for applications requiring fine adjustments.
Integrated Design: Combines gearing, bearings, and often sealing into a single, pre-assembled, and pre-lubricated unit, simplifying installation and reducing maintenance points.
Robust Construction: Utilizes high-strength materials (case-hardened steels, specialized alloys) and precision manufacturing processes for durability in harsh environments (dust, moisture, temperature extremes).
Self-Locking Capability (Often): Many designs, particularly single-start worm gears, offer inherent self-locking properties, preventing back-driving and holding position securely without needing an external brake (though a brake is still recommended for safety-critical holds).
High Efficiency (Modern Designs): Advanced manufacturing techniques, optimized gear tooth profiles, and high-quality bearings contribute to significantly improved efficiency, reducing power loss and heat generation.
Primary Applications of S Slew Drives
The unique capabilities of S Slew Drives make them indispensable in numerous sectors requiring robust, precise rotation:
Solar Energy: The dominant application, driving the precise azimuth and elevation tracking movement of solar panels in photovoltaic (PV) and concentrated solar power (CSP) plants to maximize sun exposure throughout the day.
Heavy Construction Machinery: Providing the rotational power for excavator upper structures, crane booms and hooks, drilling rig masts, and concrete pump booms, handling immense loads and dynamic forces.
Wind Energy: Used in yaw systems to rotate nacelles into the wind and pitch systems to adjust blade angles for optimal power generation and storm protection.
Material Handling: Enabling rotation in ship-to-shore cranes, RTG (Rubber-Tyred Gantry) cranes, stacker-reclaimers, and automated warehouse systems.
Industrial Automation & Robotics: Facilitating precise indexing and positioning in heavy-duty turntables, welding positioners, large manipulators, and assembly line equipment.
Defense & Aerospace: Employed in radar antenna positioning, missile launcher traversal/elevation, and other critical motion control systems requiring reliability under stress.
Medical Imaging: Powering the rotation of heavy CT and MRI scanner gantries with smoothness and precision.
Factors Influencing S Slew Drive Pricing
The cost of an S Slew Drive is determined by a complex interplay of technical specifications and commercial factors:
Torque & Load Ratings: Higher required torque output and load capacities (axial, radial, moment) necessitate larger, more robust components (gears, bearings, housing), significantly increasing material and manufacturing costs.
Precision & Accuracy Requirements: Demands for ultra-high positioning accuracy, low backlash, and smoothness require more advanced manufacturing techniques (grinding vs. hobbing), tighter tolerances, and higher-grade components, driving up price.
Size & Weight: Larger diameter slew drives inherently require more material and more complex machining/fabrication processes.
Gear Type & Ratio: The complexity of the gear set (e.g., single-start vs. double-start worm, helical variants), gear ratio, and manufacturing precision impact cost. Higher ratios often require larger worm wheels.
Bearing Type & Size: The choice and size of the main rotational bearings (crossed roller bearings vs. large diameter slewing rings, multiple rows) are major cost factors. Larger, higher-capacity bearings are exponentially more expensive.
Materials & Heat Treatment: Use of premium alloy steels, specialized surface hardening processes (case hardening, induction hardening), and advanced corrosion protection coatings add to the cost.
Sealing & Environmental Protection: Requirements for high IP ratings (dust/water ingress protection), operation in extreme temperatures (-40°C to +80°C+), or corrosive environments necessitate specialized seals, lubricants, and surface treatments.
Customization: Modifications from standard catalog designs (special flanges, mounting holes, shaft configurations, integrated sensors, unique lubrication systems, special paint) incur additional engineering and production costs.
Certifications: Compliance with stringent industry standards (ISO, CE, DNV-GL, etc.) or specific customer quality management systems adds verification and documentation costs.
Order Volume & Supply Chain: Economies of scale apply; larger orders typically have lower per-unit costs. Market fluctuations in raw materials (steel, bearings) and component availability also influence pricing.
Manufacturer Expertise & Reputation: Established manufacturers with proven reliability, extensive testing facilities, and strong technical support often command a premium reflecting the value of reduced risk and downtime.
Supplier of S Slew Drive
LYRADRIVE stands as a prominent global designer and manufacturer of high-performance slew drives and precision slewing bearings. Renowned for engineering excellence, LYRADRIVE offers a comprehensive range of standard and fully customized solutions tailored to meet the most demanding torque, load, and environmental specifications across diverse industries. Their commitment to rigorous quality control, advanced manufacturing processes, and robust material selection ensures products deliver exceptional reliability and longevity in critical applications worldwide. LYRADRIVE provides extensive technical support, from initial design consultation through installation guidance and after-sales service, making them a trusted partner for engineers seeking optimal rotational drive solutions. Their drives are integral components in solar trackers, heavy machinery, cranes, and numerous other applications requiring dependable, high-capacity rotation.



