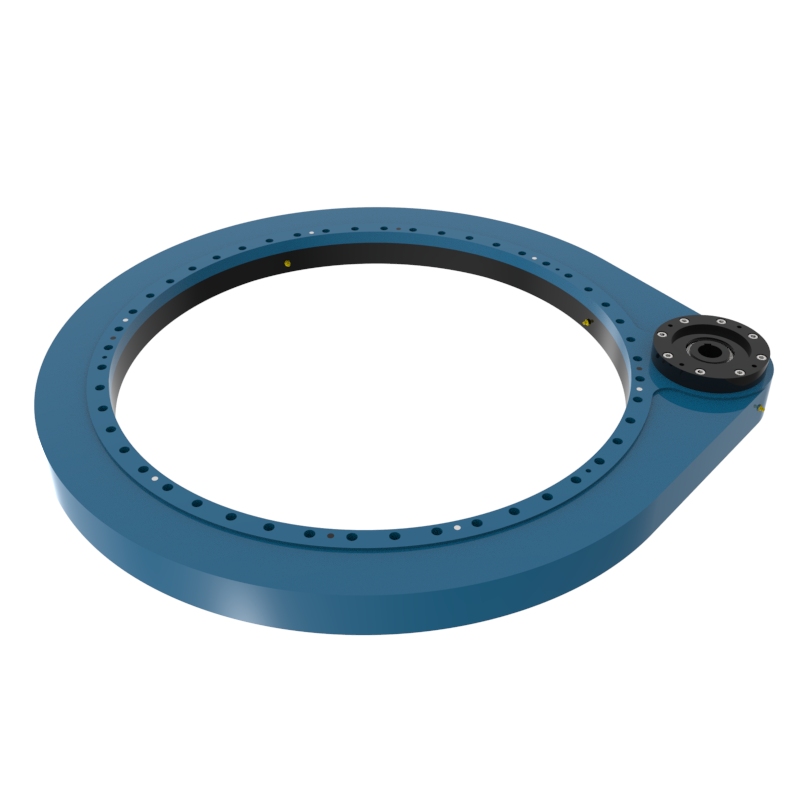
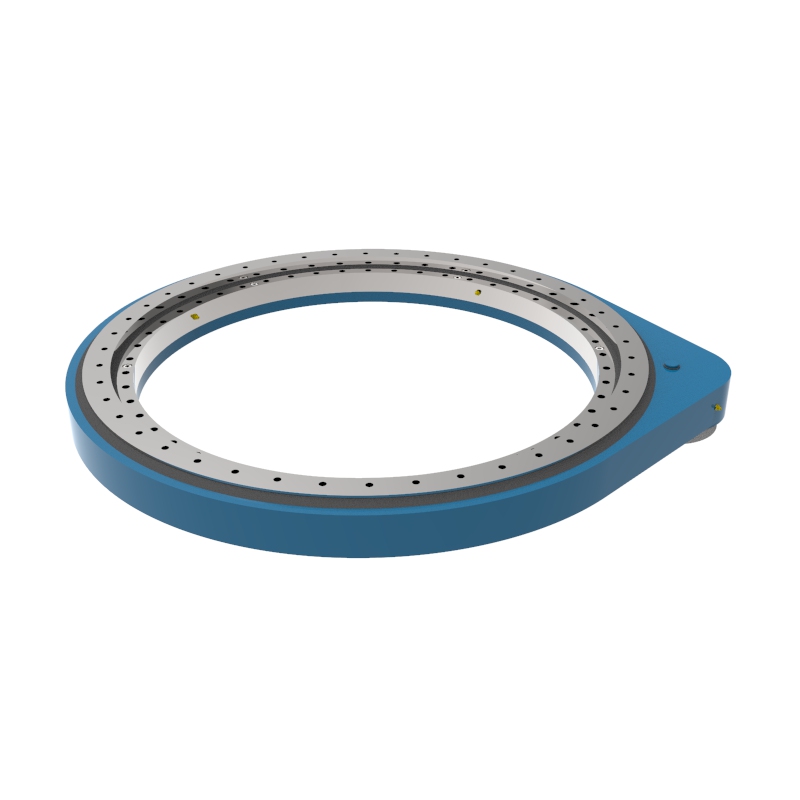
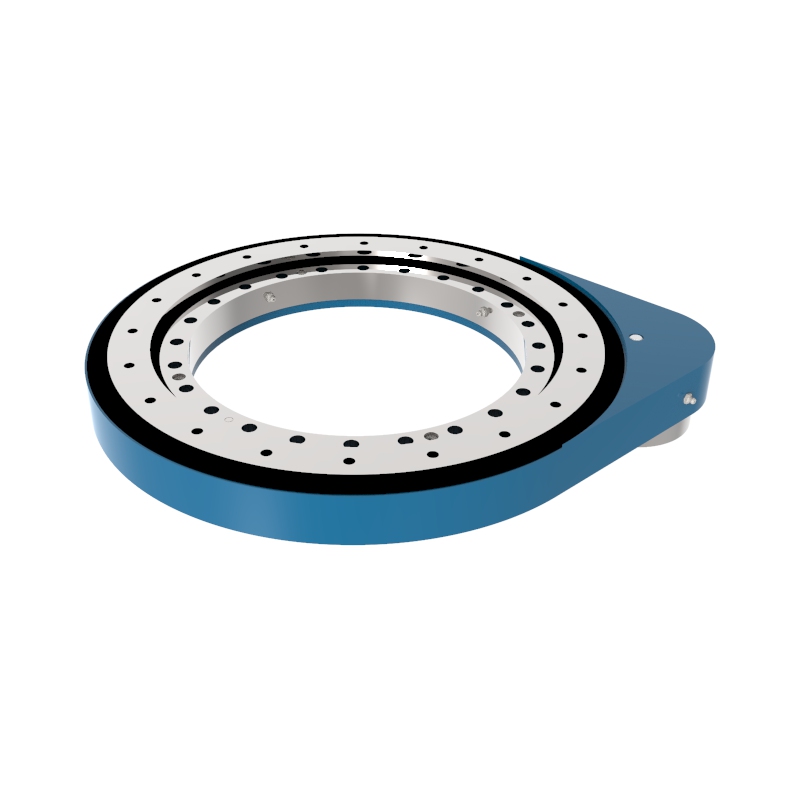
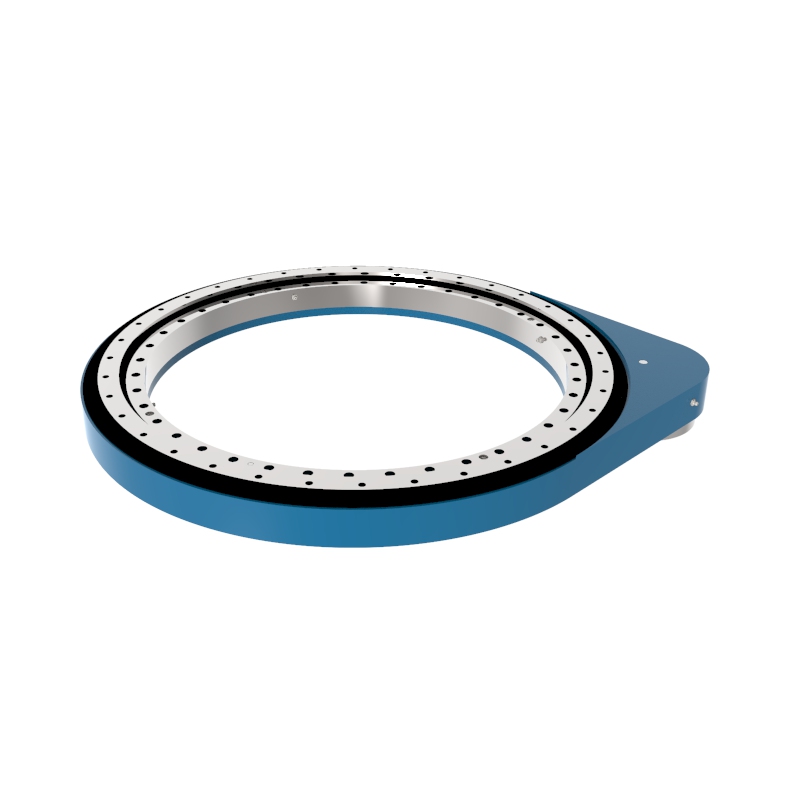
A Spur Gear Slew Drive is a variant of traditional slew drives that uses spur gears instead of the more common worm gears. Slew drives are mechanisms designed to handle both rotational motion and heavy loads, and they are typically comprised of a gear (the driving mechanism), a slewing ring (the bearing that also acts as a structural component), and a housing that holds these components together.
Medium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0741
SP-M 0741 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wide
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0841
SP-M 0841 gear slewing drive is an efficient medium-sized gear reduction transmission device, which
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 0941
SP-M 0941 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wid
Read More Get A QuoteMedium Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-M 1091
SP-M 1091 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is wid
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0455
The SP-H 0455 gear-type slewing drive is a high-efficiency, heavy-duty gear reduction device common
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0555
SP-H 0555 gear slewing drive is a heavy-duty and efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in crane slewing and heavy machinery slewing platforms, especially in working conditions that require high precision and have limited insta
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0955
SP-H 0955 gear slewing drive is a heavy-duty and efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in crane slewing and heavy machinery slewing platforms, especially in working conditions that require high precision and have limited insta
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0855
SP-H 0855 gear slewing drive is a heavy-duty and efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in crane slewing and heavy machinery slewing platforms, especially in working conditions that require high precision and have limited insta
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0755
SP-H 0755 gear slewing drive is a heavy-duty and efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in crane slewing and heavy machinery slewing platforms, especially in working conditions that require high precision and have limited insta
Read More Get A QuoteHeavy Duty Gear Slewing Drive SP-H 0655
SP-H 0655 gear slewing drive is a heavy-duty and efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in crane slewing and heavy machinery slewing platforms, especially in working conditions that require high precision and have limited insta
Read More Get A QuoteLightweight Slewing Ring Gear Drive SP-I 0941
SP-I 0941 gear slewing drive is a highly efficient gear reduction transmission device, which is widely used in the automatic slewing of industrial machinery, especially in the occasions that require high precision and high speed.
Read More Get A Quote
Design of Spur Gear Slew Drive
Spur Gears: Unlike worm gears that provide high reduction ratios and non-back drivability, spur gears are straight-toothed gears. In a slew drive, these gears mesh with the external ring gear of the slewing bearing.
Slewing Ring: This is typically a large diameter bearing that accommodates axial, radial, and moment loads. The gear teeth are often fabricated on the inner or outer ring of the slewing bearing.
Drive Mechanism: The drive mechanism in spur gear slew drives typically involves a pinion (a small spur gear) that drives a larger gear integrated into the slewing ring. This setup can be powered by electric or hydraulic motors.
Advantages of Spur Gear Slew Drive
Efficiency: Spur gears are more efficient than worm gears, particularly at higher speeds, because they have less friction and heat generation during operation.
Speed: They can handle higher rotational speeds than worm gear slew drives due to their efficient power transmission.
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, spur gears are simpler and cheaper to manufacture compared to worm gears.
Backdrivability: While this can be a disadvantage in some applications, the ability to backdrive can be beneficial in scenarios where manual movement of the driven load is necessary.
Disadvantages of Spur Gear Slew Drive
Noise: Spur gears are typically noisier than worm gears, especially at high speeds.
Backdrivability: In applications where holding torque is crucial (like in some lifting operations), the natural backdrivability of spur gears can be a drawback as it might require additional braking or locking mechanisms.
Typical Applications of Spur Gear Slew Drive
Cranes and Lifting Equipment: Used in the rotation mechanisms of cranes where high speed and efficiency are important.
Antenna Positioning: In communication systems where quick and precise adjustments are needed.
Industrial Turntables: Where heavy loads are rotated at moderate to high speeds.
Automation and Robotics: In manufacturing settings where components need to be rotated quickly and accurately.
Wind Turbines: For yaw and pitch control mechanisms where efficiency and speed are critical.
Selection Considerations
When selecting a spur gear slew drive, consider the operational requirements such as load capacities, speed, precision, environmental conditions, and space constraints. Also, evaluate the need for additional systems like brakes or locks if backdrivability is a concern.
In summary, spur gear slew drives offer a robust and efficient solution for applications requiring rotational motion handling under various loading conditions. They are particularly suited to applications where speed and efficiency are more critical than the self-locking capability of worm gears.
Spur Gear Slew Drive Installation and Operation Manual
Before installing the Spur Gear Slew Drive, please read this manual.
This manual contains essential information for proper installation and maintenance.
All following procedures must be performed by qualified personnel.
For technical issues, contact our after-sales service immediately.
1. Transportation, Handling, and Storage
1.1. Transportation and Handling
During transportation, ensure the Spur Gear Slew Drive packaging is oriented correctly to avoid impacts. Wear work gloves when handling and operate with care. The Spur Gear Slew Drive typically has threaded holes on the outer ring. Use at least three lifting eyes with a hoisting device for safe handling.
1.2. Storage
Store the Spur Gear Slew Drive in its original packaging, placed in a dry, ventilated area. In sealed packaging, the anti-rust protection lasts 6 months. For longer storage, take additional protective measures.
2. Installation and Maintenance
2.1. Pre-Installation Checks
Inspect the Spur Gear Slew Drive for physical damage. Clean the Spur Gear Slew Drive and mounting brackets, removing debris (e.g., metal shavings, burrs, paint, welding slag).
2.2. Cleaning Anti-Rust Oil from Mounting Surfaces
Use cleaning solvents (e.g., diesel, gasoline) to remove anti-rust oil from external surfaces. Avoid solvents that degrade rubber seals. Follow solvent safety guidelines for worker protection.
2.3. Bolt Selection
Our company does not supply assembly bolts. The following are recommendations only:
a. Select bolts of correct size, type, and strength grade.
b. Minimum bolt grade: 8.8.
c. Thread engagement length: 2× nominal bolt diameter.
d. Avoid bolt protrusion beyond threads to prevent interference or damage.
e. If contact stress exceeds limits, use high-strength washers.
2.4. Bolt Tightening Torque
Refer to the table below (values in N·m):
| Bolt Size | 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | Bolt Size | 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M4 | 2.25 | 3.31 | 3.87 | M16 | 168.00 | 246.00 | 288.00 |
| M5 | 4.16 | 6.77 | 7.92 | M18 | 229.00 | 336.00 | 394.00 |
| M6 | 7.80 | 11.50 | 13.40 | M20 | 327.00 | 481.00 | 562.00 |
| M8 | 19.10 | 28.00 | 32.80 | M22 | 450.00 | 661.00 | 773.00 |
| M10 | 38.00 | 55.80 | 65.30 | M24 | 565.00 | 830.00 | 972.00 |
| M12 | 66.50 | 97.70 | 114.00 | M27 | 837.00 | 1230.00 | 1439.00 |
| M14 | 107.00 | 156.00 | 183.00 | M30 | 1131.00 | 1661.00 | 1944.00 |
2.5. Spur Gear Slew Drive Installation
Follow these steps to avoid internal stress or installation issues:
a. Apply thread-locking adhesive.
b. Pre-tighten bolts crosswise (see diagram). Start at the inner/outer ring, tighten diagonally to 30% torque, then 50%, and finally 100%.
c. Install all bolts. If structural constraints prevent full installation, seal unused holes (e.g., with silicone) to prevent water/dust ingress.
d. Ensure bolt length does not interfere with rotation.
e. Mark bolt heads and joints after tightening to check for loosening later.
2.6. Lubrication
Critical components are pre-lubricated with Mobil EP2 grease. Re-lubricate during installation if needed:
a. Gear raceway: Pre-lubricated.
b. Gear meshing area: Pre-lubricated.
c. Support bearings: Pre-lubricated.
2.7. Re-Lubrication Intervals
Intervals depend on operating conditions. Conduct tests for precise timing. General guidelines:
| Working Conditions | Interval |
|---|---|
| Indoor (industrial positioners, robots, etc.) | Annually |
| Harsh outdoor (cranes, wind/solar systems) | Annually |
| Extreme climates (marine/desert/polar) or >70h/week | 6 months |
| Severe environments (mining, steel mills, oil fields) | 2 months |